Service Manual Suzuki Carry 1000
Suzuki Carry (DA62T) & Every (DA64) vans — front view Overview Manufacturer Also called Suzuki Every Suzuki Every Wagon Suzuki Super Carry Bedford/GME/Vauxhall Rascal Holden Scurry Maruti Omni Maruti Versa Wuling Rongguang Daewoo Damas Chevrolet CMV/CMP Mitsubishi Colt T120ss Chang'an SC6320G/Chana Star Hafei Songhuajiang HFJ6350 SYM T880/T1000/V5/V9/V11 Chevrolet N300 Max Ford Pronto Chevrolet Super Carry Hanjiang SFJ1010/SFJ1011/SFJ1012 (pick-up truck, China) Hanjiang SFJ 6320/6322/6323 (van, China) Production 1961–present Body and chassis The Suzuki Carry is a produced by the automaker. The version was originally called the Carry van until 1982 when the was renamed as the Suzuki Every (: ). In, the Carry and Every are but the Suzuki Every Plus, the bigger version of Every, had a longer for safety purposes and a larger 1.3-liter 86 hp (63 kW) four-cylinder engine. They have been sold under a myriad of different names in several countries, and was the only car offered with and badges. Contents.
Introduction In their home market, the Carry truck and van (and Every van) compete with a number of similarly sized vehicles, such as the, and the. Some of these are also competitors in export markets, mainly the Carry and the Hijet. The first two generations of Carrys were sold with the badge rather than the company name Suzuki, emphasizing their focus on 'Light Cars' (better known as ). Suzulight FB/FBD First generation. 1964–1965 Suzulight Carry Van FBD Overview Also called Suzulight Carry Production 1961–1965 Assembly, Japan Body and chassis 2-door 3-/4-door Powertrain 359 cc The Carry series was born in October 1961 with the FB Suzulight Carry, a with the engine underneath the front seat but with a short.
The layout has been referred to as a '. The FB Carry underwent some light modifications in October 1963, for the 1964 model year. A glassed FBD Carry Van was added in September 1964.
The engine too was called the, a 359 cc (21.9 cu in) air-cooled, two-stroke with 21 hp (16 kW). This engine remained in use, in form, until late 1987 in the (as the LJ50). Top speed was no more than 76 km/h (47 mph). FB suspension was rigid with leaf springs, front and rear. A panel van (FBC) was also available from July 1962.
1965–1969 Suzulight Carry L20 Overview Also called Suzulight Carry Production 1965-1969 Assembly, Japan Body and chassis 2-door 4-door Powertrain 359 cc In June 1965 the rebodied L20 Suzulight Carry replaced the FB. The ladder-frame chassis was modified, now with independently sprung front wheels (by torsion bars). While output remained 21 hp, the engine benefitted from Suzuki's patented CCI (Cylinder Crank Injection) lubrication system.
The Carry Van was replaced by the new L20V in January 1966, and there was also a (L21). Finally, there was the L20H, a pickup with a canvas canopy and a rear-facing seat placed in the bed, providing seating for four. Top speed for the second generation was down to 75 km/h. The Carry Van had a horizontally divided two-piece tailgate, and sliding rear windows.
Production of this more traditional version continued in parallel with the cab-over L30 Carry, ending only with the 1969 introduction of the L40. 1966–1969 Suzuki Carry L30 Overview Production 1966-1969 Assembly, Japan Body and chassis 4-door 2-door Powertrain 359 cc The new '30 Suzuki Carry (the 'Suzulight' label was being retired) was a full cab-over design, with the same mounted horizontally underneath the load area. The starter and generator were combined and mounted directly on the front of the crankshaft. Introduced in February 1966, the L30 was built alongside its more traditional predecessor until they were both replaced by the L40. A canopied L30H, similar to the L20H but with the seats in the bed facing each other, was available right from the start.
There was also an L31, with a drop-side bed. Performance and mechanics were very similar to its bonneted sister, but the load area was considerably larger. Maximum load capacity was still 350 kg (770 lb). A short-lived Carry Van version of the L30 (L30V') was not introduced until March 1968, but offered four doors and a two-piece tailgate (top and bottom). Bodywork was the same ahead of the B-pillar. Suzuki Carry L40 rear In July 1969 the designed L40 Carry was introduced.
In November of the same year, a van version with two opening side doors and a top-hinged rear gate was added. Giugiaro's design was more obvious in the Carry Van iteration, very symmetrical with similar looks to the front and rear. The L40's design was not overly utilitarian, limiting interior space and being a bit too modern for the usually very orthodox Japanese commercial customer base. On the other hand, the L40 did benefit from an updated, 25 PS (18 kW) version of the now venerable FB engine. Dimensions, dictated by regulations, remained 2,990 mm × 1,295 mm (117.7 in × 51.0 in) and 359 cc (21.9 cu in).
Free Suzuki Service Manuals
Max load was 350 kg (770 lb) for the truck, and 300 kg (660 lb) for the van versions. Top speed increased considerably to 95 kilometres per hour (59 mph). As part of a minor facelift in April 1971, the Carry received a 27 PS (still at 6,000 rpm) version of the well-known FB engine, featuring Suzuki's CCIS (Cylinder Crank Injection and Selmix) lubrication system. This engine also found its way into the recently introduced. Torque was 3.7 kg⋅m (36 N⋅m; 27 lb⋅ft) at 5,000 rpm. There was also a Panel Van version, with a boxy unit mounted on the rear of a Carry truck chassis.
In 1971, a V40FC Camper version of the Van was also added. While the truck versions were replaced in May 1972, the L40V continued for another three months before an L50 Van took its place. 1975-1976 Suzuki Carry L50 (facelift) Overview Production 1972-1976 Assembly, Japan Body and chassis 5-door 2-door Powertrain 359 cc 596 cc two-stroke I2 The fifth generation L50 Carry debuted in May 1972, followed by a new Carry Van in August. The new model echoes Giugiaro's design, but without ventilation windows in the front doors and with a more traditional appearance.
Headlights are now round, while the van version receives a more square rear body and with a sliding rear side door. The engine is a water-cooled design , otherwise similar to the previous engine but now with 28 hp (21 kW). Max load was back up to 350 kg (770 lb). In December 1972, a five-door van (L50VF, with sliding side doors) was added. Three months later, the dropside L51 went on sale.
In November 1973 the Carry underwent a minor facelift, receiving a new grille and modified front bumper. The interior was also updated, with a new dashboard and finally hanging gas and clutch pedals.
The fifth generation Carry led Suzuki to great market success, with Suzuki selling more kei trucks than all others during 1973 and 1974. In September 1975 a special export version was introduced, aimed at customers who wanted more loading ability. The new L60 series received a larger, 446 cc (also ) version of the L50.
29 PS (as opposed to 26 for export market 360 cc models), a stronger differential 'to transmit the generous torque' and sturdier springs meant load capacity increased to 550 kg (1,210 lb). For 1975, the Carry received minor changes allowing for the fitment of new larger license plates. In December 1975, the domestic market L50s' engine lost two horsepower (down to 26) in the effort of fulfilling new, stricter emissions standards. 1,295 mm (51.0 in) (ST10). 1,395 mm (54.9 in) (ST20) In May 1976, responding to changed standards for the Kei class, Suzuki released the Carry 55, chassis code ST10/ST10V.
It had the larger, water-cooled but still two-stroke three-cylinder engine of 539 cc but was otherwise hard to distinguish from the preceding L50 series. The only two differences in appearance were bigger (albeit slimmer) bumpers which no longer enveloped the bottom of the front, as well as slightly altered doors with a slight bump in the swage line to accommodate the door handle. There was also an ST11 version with a drop-side bed. The ST10 (along with the ) was the first Suzuki to enter CKD production in Indonesia, in 1976. In 1977 it was replaced by the larger ST20. Suzuki Carry ST20 used as a, rear view Soon thereafter, in September 1976, the interim ST10 (only built for four months) was gradually replaced by the widened and lengthened ST20 pickup version which also has a longer wheelbase.
Marketed as the Suzuki Carry Wide 550, it now reached the maximum dimensions set for the Kei class. In November, the ST20 Van took its bow - this version was 4 cm (1.6 in) shorter than the truck as it reused the shorter rear side bodypanels of the L50 and ST10 versions.
Some special variants of the ST10 (such as refrigerated versions, panel vans, etcetera) remained on sale alongside the ST20 for a little while longer until new versions could be developed. There was also an ST20K model available. The 'K' referred to the 'trucklike' nature of the vehicle in that it had three drop-sides as opposed to the utility version which had only a tailgate and formed sides. The ST20 range retained the three-cylinder 539 cc two-stroke engine of the ST10 and has a carrying capacity of 350 kg (772 lb). Maximum power remained 26 PS (19 kW) at 4500 rpm. In October 1977, after about 187,000 had been built, the ST20 underwent a light facelift, with increased equipment and all versions (excepting the base truck) now featuring a front grille.
Equipment levels were base, Standard, and Super Deluxe. The base version has no front grille, the Standard has a black grille, while the Super Deluxe features chrome trim on the grille as well as chromed hubcaps.
By October 1977, the Custom Van was available in the Japanese market. Well equipped, with metallic paint, reclining fabric-covered seats, and chrome bumpers, this was aimed squarely at use as a private car. This heralded the development of the future 'Every' range of passenger microvans. By 1977, the export only ST80 appeared - this version was the first Carry to be equipped with a four-stroke engine, the inline-four 797 cc as recently introduced in the. In the Carry, however, the engine only developed 37 hp (28 kW; 38 PS) at 5500 rpm.
The ST20 Carry was also produced in Indonesia from 1978 until at least 1983, where it was nicknamed 'Turungtung'. This is an word for the sound made by the Carry's two-stroke engine. The ST20 Carry was the first Suzuki product to be built in Indonesia, where it saw extensive use as an.
The ST20 was only offered as a truck in Indonesia, but local body builders such as Adiputro and Liling Putra came up with multi-seat taxi bodies and other variations. The Indonesian ST20 has a claimed 33 PS (24 kW) at 4500 rpm and 52 N⋅m (38 lb⋅ft) of torque at 3000 rpm, being unaffected by emissions regulations. Chang'an SC1011 Suzuki Bolan In Pakistan, a small affiliate of the, still assembles and distributes the Suzuki Bolan, based on the ST90V version of the Carry (also known as Hi-Roof) with the three-cylinder 796 cc carburetor engine with output of 37 hp (28 kW). The four-speed manual transmission allows for a top speed of 120 km/h (75 mph). As of today it is available in two different versions VX and VXR, the better equipped VXR has got factory fitted air conditioning. The Bolan is widely used as an ambulance all over Pakistan and as a taxi in parts of the country. There is also a pickup version, called Ravi.
Ford Pronto The Ford Pronto is a rebadged Suzuki Carry ST, which was manufactured between 1985 and 2007 by, a joint venture between Ford and Lio Ho in. The Pronto was only available in the market, where it was introduced specifically to compete with 's and Sanfu's in the local market. In 2007 Ford Lio Ho ceased to produce the Pronto because the engine couldn't be made to meet revised local environmental regulations. Indonesia.
Suzuki Carrys in Indonesia are widely used as transportation minibuses known locally as ' In Indonesia the Suzuki Carry and Super Carry were assembled by beginning in 1983, fitted with the well-known 970 cc F10A engine with 50 PS (37 kW). This carried the ST100 model code, and was also available as a minivan. Thanks to a locally developed rear body with a longer overhang and a wheelbase extended by 10 cm (3.9 in), it was about 20 cm (7.9 in) longer than the Carrys sold elsewhere, which allowed a third row of seats to be fitted.
In 1986 it was updated with a new front and larger bumpers; this model was originally sold as the 'Super Carry Extra.' This model, available as a van or truck, reached 3,530 mm (139.0 in) in overall length and is 1,465 mm (57.7 in) wide. In 1989 the Super Carry received a five-speed transmission, as well as a tachometer. Although removed from the regular price lists in 2006, this version of the Carry was still built to special order until 2009, alongside the larger Carry Futura (based on the ).
Until 1987, when surpassed by the and, the Carry was Indonesia's best selling vehicle. Suzuki Super Carry. Suzuki Futura/Carry Futura/Carry 1.3 Futura/Carry 1.5 (Indonesia). (Japan). (United Kingdom). Chevrolet CMV/CMP (Central America). Chevrolet Super Carry (, ).
(South Korea). Holden Scurry (Australia). Mitsubishi Colt T120SS (Indonesia). Hafei Songhuajiang HFJ6350 (China). Chang'an SC6330 (China). (United States).
Ford Pronto (Taiwan) Production 1985-1991 1991-present (Indonesia) Assembly, Japan, Indonesia Body and chassis 2-door 5-door / or Powertrain 539 cc 543 cc I3 547 cc I3 657 cc I3 797 cc 970 cc I4 4/5-speed 3-speed Dimensions 1,840 mm (72 in) Length. 3,175 or 3,275 mm (125 or 129 in) (truck).
3,195 or 3,295 mm (126 or 130 in) (van) Width 1,395–1,475 mm (55–58 in) Height 1,675–1,800 mm (66–71 in) 600–780 kg (1,323–1,720 lb) The eighth generation Carry (and second generation Every) appeared in March 1985. It was modernized and the range again expanded, with a more powerful fuel injected engine available on top. The chassis codes became quite confusing, with DA/DB71 used for the F5A engined model (DB signifying four-wheel drive) and DA81 for the two-stroke truck which remained available until the Carry underwent a facelift in July 1986. T, B, and V suffixes were used to denote trucks, trucks with tip decks, and vans. Beginning in late 1987, a 52 PS (38 kW) turbocharged engine was available in the Every, while the Carry truck received a three-valve, supercharged version of the F5A engine with 48 PS (35 kW). There was also a short-lived nine-valve version with 32 PS (24 kW) available for better equipped versions of the Every; the regular six-valve version had to make do with 30 PS (22 kW).
In May 1989 the more modern multi-valve F5B engine entered the lineup; it received the DA/DB41 chassis code and replaced most of the F5A engines. This new engine also became available in the badge-engineered, sold by (DG/DH41). Facelift With the rules regarding the size and engines of kei-cars being altered for March 1990, Suzuki had to update the Carry/Every which now carried the DA/DB51 chassis code. A larger 657 cc engine provided somewhat more power, ranging from 38 to 58 PS (28 to 43 kW), and new more rounded bodywork provided a more modern look. The smallest engine received an upgrade in March 1991, increasing power to 42 PS (31 kW), but only six months later the DA/DB51 was replaced by the re-shelled ninth generation Carry and Every. Holden Scurry (NB) Post-1985 European market Suzuki Carrys still used the 797 cc familiar from the ST90 Carry, while Super Carrys were equipped with the 970 cc four.
Service Manual Suzuki Carry 1000
Chassis codes are SK408 and SK410, while power outputs are 37 and 45 PS respectively (27.5 and 33 kW), top speeds 110 and 115 km/h. Heftier bumpers meant overall length was up 10 cm, for a total of 3295 mm. Production of export models began in July 1985. The SK408 (sometimes called the DA11) was discontinued in October 1989.
Later Super Carrys received the same 1.3 liter inline-four as fitted to the. In much of Europe this generation of the Carry was also sold as the Bedford, Vauxhall, or GME Rascal. These were built at the GM plant in Luton, to circumvent JAMA's voluntary export restrictions. In Australia this model was sold as both the Super Carry (in ute, van, or wagon form) and as the Holden Scurry, which was not available as a 'ute'. In Australia, the Scurry was designated as the NB series.
Suzuki 1000 For Sale
The Super Carry continues in production in Vietnam for local markets, as a truck or panel van, with a emissions compliant engine. The 970 cc engine has electronic fuel injection and develops 31 kW (42 PS) at 5500 rpm. The 3,240 mm (128 in) long truck is the biggest selling truck in Vietnam and the engine was updated to meet the Euro 4 emissions standards in 2017. Indonesia. Mitsubishi Colt T120SS (1991-2005 version) In Indonesia, the Suzuki Carry received a redesign which had its premiere in mid-February 1991.
This was a response to the 1989 introduction of the 1.3 liter; somewhat larger it was now 3,700 mm (146 in) long and also ten centimeters wider than before. This has a wheelbase of 1,970 mm (78 in), it is 3,875 mm (153 in) and 1,570 mm (62 in) wide. It has a 1360 cc engine, later enlarged to 1493 (sometime in the late 90s) and then 1590 cc. Internal codenames for these models are ST130, ST150, and ST160, while the original Suzuki Carry Futura was also referred to as the SL413.
Beginning in 1994, the rear doors received wind-down rather than sliding windows. In March 2005, the 1.5 engine was upgraded to fuel injection rather than the earlier carburettors. Unlike the Mitsubishi version, Suzuki also offers a factory-bodied minibus version. For the Indonesian market, The Suzuki Futura is also offered as the Mitsubishi Colt T120SS MPi. The name is a continuation of the first generation, which was marketed as the 'Colt T120' in many countries including Indonesia. When production began in 1991 it replaced the Minicab-based 'Jetstar'. The T120SS is based on the locally developed Suzuki Carry Futura (later just Futura), with which it shares everything aside from the engines.
Overall length is 3720 mm (3940 mm for the '3-way wide deck' version). The Colt T120SS is available as either a bare chassis, a fixed-side pickup truck, or one where all three sides fold down, called '3-way wide deck'. The engine used is either Mitsubishi's 1.3 L (1,343 cc) carburetted or the bigger 1.5 L (1,468 cc) fuel injected. The smaller engine puts out 78 PS (57 kW) at 6000 rpm.
This engine had the same specs from its time of introduction in 1991 until it was replaced in 2005, except for one major difference: in 1996 it was redesigned and is no longer an. The larger unit, which meets Euro 2 emissions standards, produces 86 PS (63 kW) at 5750 rpm. Both engines feature three valves per cylinder.
The bigger engine arrived in March 2005 with 1.5-litre Multi Point Injection, when the T120SS was also lightly facelifted, with a new grille featuring a triangular central portion. The bare chassis version is usually converted into a microbus by local bodybuilders, for use as an Angkot,.
The Indonesian Suzuki Carry Futura was facelifted several times, in August 1997, March 2005 and April 2010, and was facelifted again in January 2017, with a redesigned grille and bumper. While the Mitsubishi T120ss received facelift in 2005. Starting in 2016, Maruti Suzuki has produced a rebadged version of the Carry Futura in India as the.
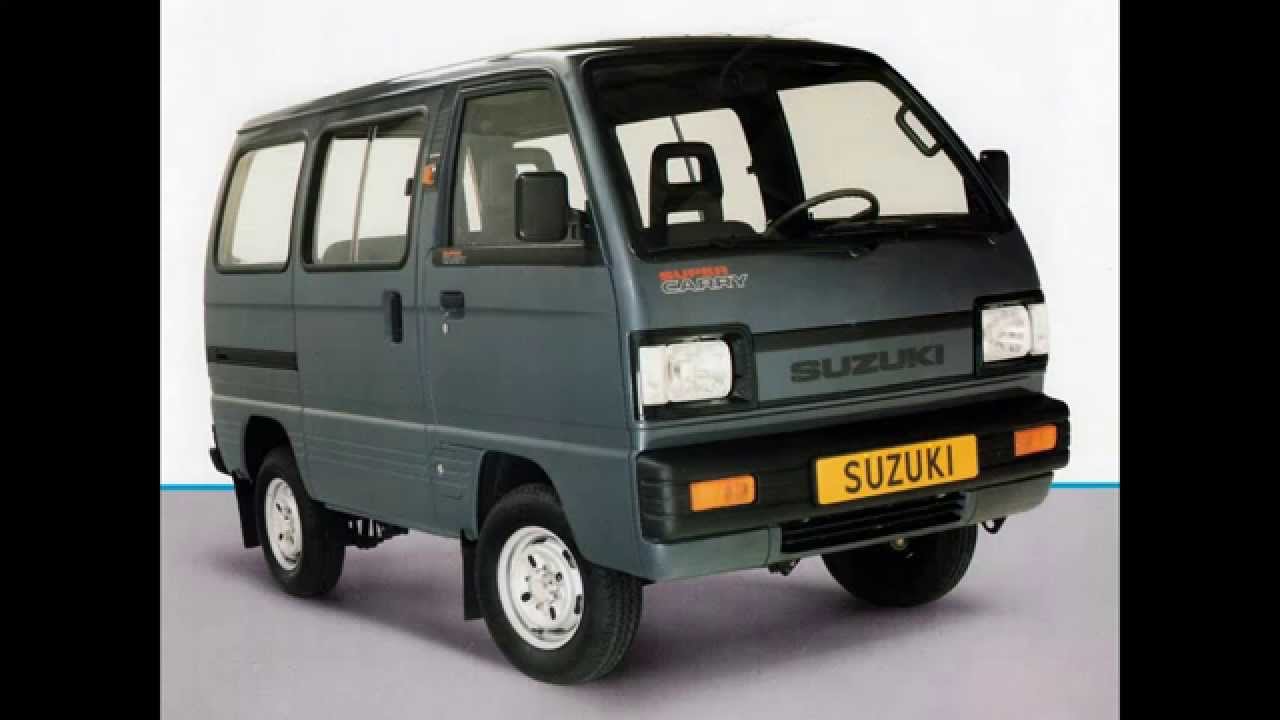
This model receives the same 793 cc diesel twin as Filipino models, or the CNG-powered 1.2-liter inline-four. Philippines The larger, Indonesian-developed Super Carry is also assembled in the Philippines. The locally developed turbodiesel version appeared in late October 2016, with a 793 cc (48.4 cu in) two-cylinder engine with 32 PS (24 kW) at 3500 rpm. It is available as a flat-bed truck, utility van, cargo van, or prepared to be fitted with bodywork. It is 3,800 mm (149.6 in) long, with a wheelbase of 2,110 mm (83.1 in), a cargo bed of 2,384 mm (93.9 in), and can take a load of 625 kg (1,378 lb) as well as two occupants. Bedford Rascal Bedford Rascal Overview Manufacturer / Also called Vauxhall Rascal GME Rascal Production 1986–1993 (England) 1993–1999 (Japan) Assembly, Body and chassis 5-door 2-door Powertrain 970 cc (1.0 L) 4/5-speed manual Dimensions Length 3,295 mm (129.7 in) Width 1,395 mm (54.9 in) Height 1,780 mm (70.1 in) 755 kg (1,664 lb) Chronology Successor The Bedford Rascal (later Vauxhall Rascal), also built as the Suzuki Super Carry, was a and that was developed as a joint venture between the car company (GM) and the automaker. It was sold under GM's British-based marque as well as in Suzuki form.
Other names were used in a few international markets, such as GME (General Motors Europe) for those continental European markets where Suzukis were generally not marketed and where the 'Bedford' and ' brands were largely unknown. The van was produced at the plant in, England, adjacent to the main Vauxhall factory (GM's British-based passenger car marque). Alongside the Bedford, the Suzuki-branded twin was manufactured for the European market (where Bedford is a less established brand). Sold from 1986 to 1994, the Rascal, like the Super Carry, was a small and economical van intended for many purposes. The vehicle's strengths were its diminutive size and maximum payload weight; 550 kg for the van and 575 kg for the pickup.
The principal visible difference between Bedford and Suzuki versions is the front trim: the Super Carry has two separate plastic headlamp surrounds and the Rascal has a single full width one with 'Bedford' moulded in the middle. Timeline:. 1986: launched. 1990: re-badged as the Vauxhall Rascal, as the Bedford marque was being retired. 1993: production moved to Japan, where the vehicle was made until 1999. Mostly sold as; and versions were also made.
Ninth generation (Autozam Scrum) Overview Also called Changan SC6331 Ford Pronto Production 1991-1999 Assembly, Japan Body and chassis 2-door 4-door /, / (Carry), / (Every/Carry Van) Powertrain 657 cc 5-speed 3-speed Dimensions 1,855 mm (73 in) (Carry) 2,000 mm (79 in) (Every/Carry Van) Length 3,295 mm (130 in) Width 1,395 mm (55 in) Height 1,715–1,865 mm (68–73 in) 650–720 kg (1,433–1,587 lb) The ninth generation Carry (and third generation Every) appeared in September 1991. The 657 cc F6A engine remained from the previous generation, but an all-new bodywork was much smoother, originally with slim, small rectangular headlights. The chassis was largely unchanged for the truck (albeit with a somewhat longer wheelbase), but the vans had a considerably longer wheelbase and an engine mounted midships, just ahead of the rear axle. Chassis codes changed accordingly, and were now different for the Carry and the Every. The trucks are DC/DD51T and the vans are DE/DF51V ('DD' and 'DF' for four-wheel drive versions).
Two different front treatments were available, one with small rectangular aerodynamic headlights and one with large, round units (used on lower-spec models). The ninth-generation Carry received a very gentle facelift in September 1993, which meant that the front drum brakes were switched to discs on all models. Two months later the Carry Van line switched to the Every nameplate and the division between trucks and vans was made clearer yet. Another light change occurred in July 1995, when the front turn signals were changed from clear to amber and the bolt pattern was changed from 114.3 to 100 mm. This generation continued to be built until 1999. Most export markets continued to receive the previous generation Carry, with bigger engines and most commonly with van bodywork.
The older Super Carry is generally more rugged than the DE/DF51, which was fitted with a rear axle not as suitable for carrying heavy loads. In those rather few foreign markets where the ninth-generation Carry was available, it was sold as the SK306. In late 1997 the retro-styled Suzuki Every C arrived. 2009-2013 Suzuki Carry truck The tenth generation Carry was introduced in January 1999. It retained the F6A engine (albeit modernized) and was sold as the DA/DB52 T and V (Carry truck or Every van, 'DB' signifying four-wheel drive). This marked the end of using 'Carry' badging on vans in the Japanese domestic market. In June 1999 the DA52W (Every Wagon, only with two-wheel drive) appeared, along with the bigger Every Plus.
In 2001 a version with the more powerful timing chain equipped K6A (still of 660 cc displacement) appeared, as the DA62T/V/W. This model has also been built by (Chana) in China, as the 'Star' ( Zhixing) bus and truck (originally SC6350, SC1015). These have undergone countless revisions and enlargements and still form the basis for much of Chang'an's light truck production, The Carry truck was completely rebodied in May 2002, but the existing Every Van and Wagon continued to be produced until replaced in August 2005, as the two lines continued a process of divergence begun with the introduction of the Every in 1982. Export versions Early Suzuki Carrys are popularly called 'half loafs' in South Africa, referring to 'half a loaf of bread' (still a staple of many South Africans). In Cape Town and Durban, many of these little vans are seen painted in bright yellow with green artwork and a chopped-off open rear end. These are part of large fleets of privately owned public transport vehicles which fit between normal taxis and city buses. Customers literally hop on the back, and pass the driver a or two, and simply jump off at their destination.
Alternative badges The Suzuki Carry has been marketed under several different around the world: (UK), GME Rascal (France), Daewoo Damas (Worldwide), Chevrolet Super Carry (Colombia and Venezuela), Chevrolet CMV/CMP (Central America), Holden Scurry (Australia), Maruti Omni, Maruti Versa (India), Ford Pronto, Mazda Scrum, and Mitsubishi Colt T120SS. Daewoo Damas Daewoo Damas & Daewoo Labo Overview Manufacturer (1992-2011) (2011-present) Also called. Chevrolet CMV. Chevrolet CMP. Chevrolet Damas/Labo Production 1991–present AssemblyBody and chassis 4-door 2-door Powertrain 796 cc (0.8 L) The Daewoo Damas is a version of the Suzuki Carry/Every produced by the automaker since 1991. It is currently in its second generation and is available in and body styles, the latter of which is marketed as the Daewoo Labo. In some export markets, the Daewoo Damas was known as the Daewoo Attivo and since ' takeover of Daewoo it has been known in some markets, such as Central America and Tunisia, as CMV for the passenger van (Damas) and Chevrolet CMP for the pickup truck (Labo).
The Damas and Labo both come with the 796 cc engine rather than the smaller 660 cc units originally used in Japan, to provide more power and comfort. The engine was originally made for petrol but is recently only available in South Korea as an -powered unit.
The Damas is available as a 7-seat coach, 5-seat coach, or 2-seat cargo van styles and comes with various options based on DLX (deluxe) and SUPER models. The Labo is also available in STD (standard), DLX (deluxe) and SUPER models. Two main choices of the Labo body type are the and the drop-side. The pickup has an optional electric lift. The Damas is the predominant form of public transport in Uzbekistan – so much so that other buses, such as Mercedes microbuses, are called 'Big Damas'.
In Damas, generally far more than seven passengers are crammed. Both the Damas and Labos are only available with a. However, the 0.8-litre engine does not have sufficient power to both carry cargo swiftly and deliver cold air from the aircon unit at the same time without struggling. The engine struggles and shakes (potentially leading to a stall) if one tries both. However, for its purpose, the car is excellent, reliable, durable and nippy around town and outskirts, as long as speeds over 100 km/h (62 mph) are not required - beyond which the car becomes uncomfortable. The Damas and Labo are currently exempt of regulation in South Korea, which requires all of the motor vehicles produced after 2014 to have oxygen sensor installed by factory configuration.
However their production is planned to be discontinued after 2020. Of produces the Damas in complete. 2010 Daewoo Damas interior Maruti Omni Maruti Omni Overview Manufacturer Also called Maruti Van Production 1984–present Assembly, Body and chassis 4-door Related Powertrain 796 cc (0.8 L) 4-speed manual Dimensions 1,840 mm (72.4 in) Length 3,370 mm (132.7 in) Width 1,410 mm (55.5 in) Height 1,640 mm (64.6 in) 785 kg (1,731 lb) Chronology Successor The Maruti Omni is a manufactured by 's subsidiary. The first version of Maruti Omni had a 796 cc (49 cu in) inline-three engine, same as the.

Sold simply as the Maruti Van, this was the second vehicle to be launched by Maruti Suzuki. It arrived one year after the 800, in 1984.
The name was changed to 'Omni' in 1988. It received a facelift in 1998, and further minor revisions in 2005, when improvements were made to the exterior and the interior, and new colours became available. Later version of the Omni includes the:. Omni (E), released in 1996, an 8-seater version of the Omni. Omni XL - 1999, as the Omni E but with a higher roof. 1989 35hp force manuals.
Omni Cargo - 2004, created to answer the growing popularity of this car being used as an. Omni LPG - 2003, same 796 cc engine, added with a factory fitted LPG Kit, authorised by the Indian RTOs. This makes it the most economic four-wheeler in India, as far as driving costs are concerned. Omni Ambulance - A Omni E, designed for usage. This is the most common type of found in cities. The Omni could be divided into two categories: the version and the version.
The newer family version has two extra seats directly behind the front seating and facing away towards the rear of the van making it an eight seater. Older versions are modified by individual owners to add additional capacity this way. The cargo version is completely devoid of back seats. Both versions have. The Omni (E) has the following official specifications (2010). Name Vehicle specifications Max. Speed: 100 km/h (62 mph) Initial acceleration: 0-60 km/h (37 mph) in 10 seconds Fuel: Petrol Fuel consumption in city: 13–14 km/L (7.7–7.1 L/100 km) Fuel consumption on highways: 16–17 km/L (6.3–5.9 L/100 km) Power: 37 bhp (28 kW) at 5,000 rpm Construction: Cast iron Displacement: 796 cc Ignition: Multipoint fuel injection Layout: 3-cylinder in-line Max.
Torque: 62 N⋅m (46 ft⋅lbf) at 3,000 rpm Valve train: 2 valves per cylinder Transmission: Manual- 4-speed Front suspension: MacPherson strut with gas filled shock absorbers Rear suspension: Leaf spring with shock absorbers Front brakes: Booster assisted disc Rear brakes: Drum Tyres: 145 R-12 LT 6PR (radial) The initial versions were so basic that the interior dashboard even lacked a fan blower opening as a standard.